
With this method, it is not difficult to determine precise measurements.īecause it produces better resolution, reduced dead time, faster and more accurate analytical capabilities, this test is highly preferred in terms of material analysis, both qualitative and quantitative. Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) identifies the elemental composition of materials imaged in a scanning electron microscope for all elements with an atomic number greater than boron. 10s - 100s nm for EBSD, 100s nm - 5 m for EDS), and the optimum analytical conditions. The X-ray intensities are gauged by counting the photons and the obtained precision is limited through a statistical error. The spatial resolution of the 2 techniques are broadly similar (i.e. Adding to mentioned above, EDS analyses depend greatly on samples surface, homogenity, density etc. In EDX, the excess electron energy migrates to a shell in order to fill in new holes in excess of what a single X-ray can emit. X-ray or electron beam (excitation source).In an EDX system, there are four major components: Calibration and quantitative analysis: the basic theory is quite simple the ratio of the intensity of X-ray in the unknown to that of it in the standard is. EDX (aka EDS) stands for Energy Dispersive X-ray analysis, which is an analytical technique used for the elemental analysis or chemical characterization of. Every element from atomic numbers 4 to 92 can be identified under this principle, although not all methods are appropriate for light elements.
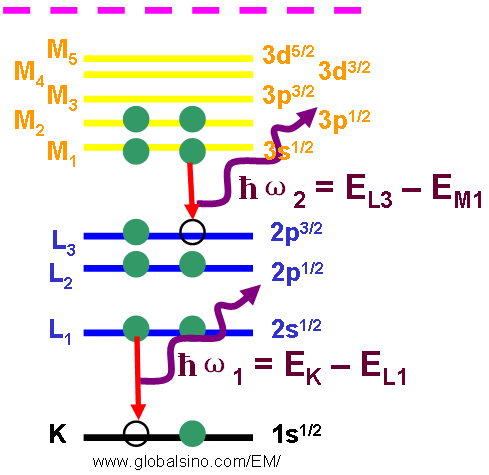
This is in order to obtain a more localized analysis of chemicals. Corrosionpedia Explains Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrography (EDX)ĮDX makes use of the X-ray spectrum that is emitted by solid samples that are bombarded through electron-focused beams.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
